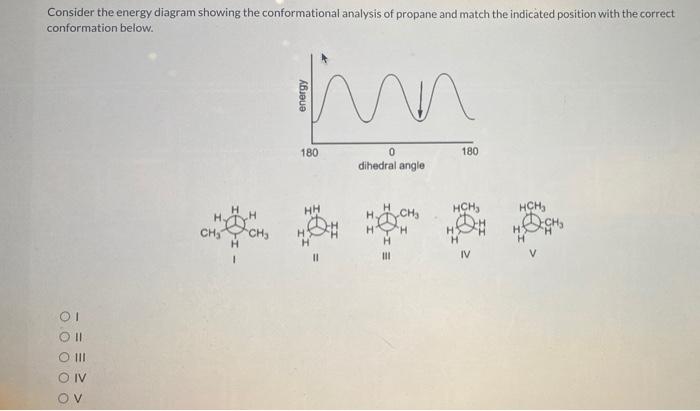
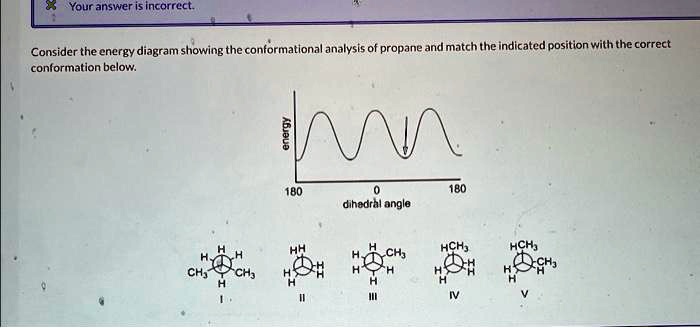
Consider the energy diagram showing the conformational analysis of propane. This diagram provides a visual representation of the different conformations of propane and their relative energies. It is a valuable tool for understanding the structure and properties of propane and other molecules.
The conformational analysis of propane is a classic example of how the rotation of bonds can affect the energy of a molecule. Propane has three carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms, and the carbon atoms are arranged in a tetrahedral shape.
The three hydrogen atoms on each carbon atom can be arranged in different ways, giving rise to different conformations of the molecule.
Conformational Analysis of Propane: Consider The Energy Diagram Showing The Conformational Analysis Of Propane
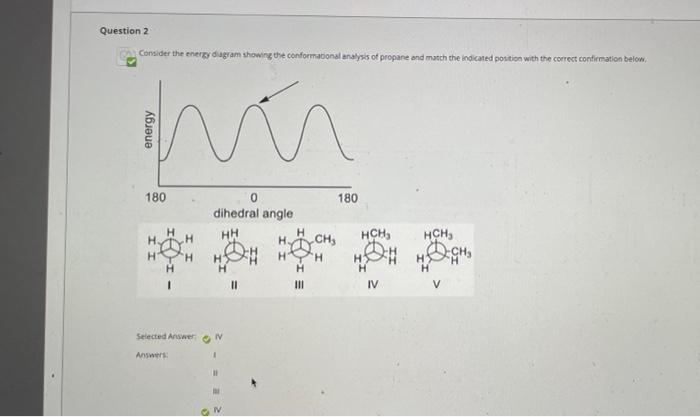
Conformational analysis is a technique used to study the different spatial arrangements of atoms within a molecule. It is important for understanding the structure and properties of molecules, as different conformations can have different energies and reactivities.
Rotational isomers are molecules that have the same connectivity but differ in their spatial arrangement. Conformational analysis involves studying the different rotational isomers of a molecule and determining their relative energies.
Energy Diagram of Propane
The energy diagram below shows the conformational analysis of propane. The different conformations are labeled and their relative energies are indicated.

The energy differences between the conformations are due to a combination of steric interactions and electrostatic interactions. Steric interactions occur when atoms or groups of atoms are too close together and repel each other. Electrostatic interactions occur between charged or polar groups of atoms.
Gauche and Anti Conformations
The gauche and anti conformations of propane are the two lowest energy conformations. In the gauche conformation, the two methyl groups are oriented at an angle of 60 degrees to each other. In the anti conformation, the two methyl groups are oriented at an angle of 180 degrees to each other.
The gauche conformation is slightly higher in energy than the anti conformation due to steric interactions between the methyl groups. The anti conformation is the most stable conformation of propane.
Eclipsed Conformation
The eclipsed conformation is the highest energy conformation of propane. In the eclipsed conformation, the two methyl groups are oriented directly behind each other. This conformation is high in energy due to steric interactions between the methyl groups.
The eclipsed conformation is rarely observed in propane because it is so high in energy. However, it can be observed in some other molecules, such as ethane.
Applications of Conformational Analysis, Consider the energy diagram showing the conformational analysis of propane
Conformational analysis has a wide range of applications in various fields, including drug design, materials science, and biochemistry.
In drug design, conformational analysis can be used to predict the binding affinity of a drug to a receptor. In materials science, conformational analysis can be used to design new materials with specific properties. In biochemistry, conformational analysis can be used to study the structure and function of proteins.
FAQ Corner
What is conformational analysis?
Conformational analysis is the study of the different conformations of a molecule and their relative energies.
What is an energy diagram?
An energy diagram is a graph that shows the energy of a molecule as a function of its conformation.
What is the gauche conformation?
The gauche conformation is a conformation in which two hydrogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are oriented towards each other.
What is the anti conformation?
The anti conformation is a conformation in which two hydrogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are oriented away from each other.
What is the eclipsed conformation?
The eclipsed conformation is a conformation in which two hydrogen atoms on adjacent carbon atoms are oriented directly behind each other.