Conduction and convection gizmo answers – In the realm of heat transfer, conduction and convection reign supreme. The Gizmo simulation offers an interactive platform to unravel the mysteries of these processes. This exploration promises a comprehensive understanding of heat flow, its underlying mechanisms, and its myriad applications.
Delving into the intricacies of conduction, we witness the direct transfer of thermal energy between adjacent molecules. Convection, on the other hand, captivates us with its intricate dance of fluid motion, carrying heat throughout substances.
Introduction
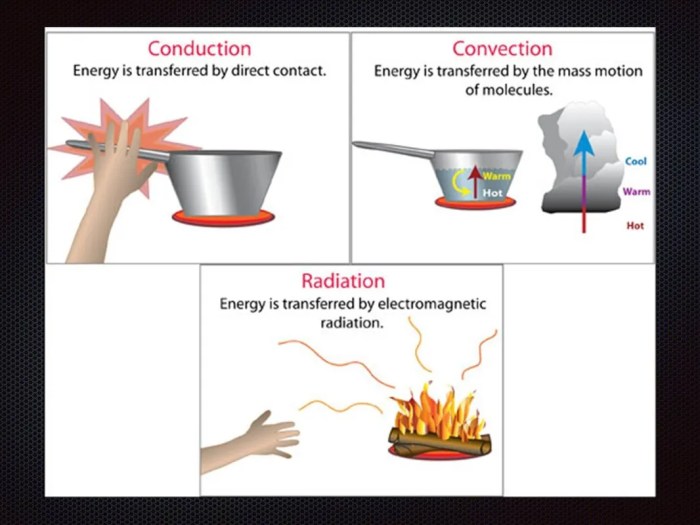
Conduction and convection are two important heat transfer processes that play a crucial role in various natural and industrial applications. This Gizmo simulation provides an interactive platform to explore these concepts and their practical implications.
The Gizmo simulation allows students to investigate the mechanisms of heat transfer through conduction and convection, observe the effects of different materials and conditions on heat flow, and understand the similarities and differences between these two processes.
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through direct contact between two objects or substances. In the Gizmo simulation, conduction occurs when a heated object is placed in contact with a cooler object, causing heat to flow from the hotter object to the cooler object until they reach thermal equilibrium.
The rate of heat transfer by conduction depends on several factors, including the temperature difference between the objects, the surface area in contact, and the thermal conductivity of the materials involved.
Examples of conduction in everyday life include:
- The transfer of heat from a hot stove to a pot placed on it.
- The melting of ice when it comes into contact with a warm surface.
- The conduction of heat through the walls of a house, keeping the interior warm during winter.
Convection
Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of fluids (liquids or gases). In the Gizmo simulation, convection occurs when a heated fluid rises, carrying heat away from the heat source, and cooler fluid takes its place. This process continues, creating a continuous flow of fluid and transferring heat throughout the system.
The rate of heat transfer by convection depends on several factors, including the temperature difference between the fluid and its surroundings, the density of the fluid, and the viscosity of the fluid.
Examples of convection in everyday life include:
- The rising of hot air from a campfire, creating a convective current.
- The circulation of warm water in a heated room, distributing heat evenly.
- The cooling of a hot cup of coffee as the warm air near the surface rises and is replaced by cooler air.
Comparing Conduction and Convection, Conduction and convection gizmo answers
Conduction and convection are both heat transfer processes, but they differ in their mechanisms and the way they occur.
| Property | Conduction | Convection |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Heat transfer through direct contact | Heat transfer through fluid movement |
| Rate of heat transfer | Depends on temperature difference, surface area, and thermal conductivity | Depends on temperature difference, fluid density, and viscosity |
| Examples | Melting of ice, heat transfer through walls | Rising of hot air, circulation of warm water |
One key difference between conduction and convection is that conduction requires direct contact between objects, while convection can occur even when there is no physical contact between the heat source and the object being heated.
Gizmo Simulation Activities
The Gizmo simulation includes several activities that help students understand conduction and convection:
- Conduction:Students can explore how different materials conduct heat by placing objects with varying thermal conductivities in contact with a heat source.
- Convection:Students can observe convection currents by heating a fluid and observing the movement of the fluid as heat is transferred.
- Comparing Conduction and Convection:Students can compare the rates of heat transfer by conduction and convection by placing objects with different thermal conductivities in contact with a heat source and observing the temperature changes.
These activities provide a hands-on and interactive way for students to learn about conduction and convection and their practical applications.
Applications of Conduction and Convection
Conduction and convection are essential heat transfer processes that have numerous applications in various fields:
- Conduction:Heat sinks in electronic devices, thermal insulation in buildings, and heat exchangers in industrial processes.
- Convection:Cooling systems in cars and computers, air conditioning in buildings, and natural convection in weather patterns.
Understanding the principles of conduction and convection is crucial for engineers, scientists, and anyone working in fields that involve heat transfer.
FAQ Summary: Conduction And Convection Gizmo Answers
What is the fundamental difference between conduction and convection?
Conduction involves heat transfer through direct contact, while convection involves heat transfer through the movement of fluids.
Can you provide an example of conduction in everyday life?
When you touch a hot stove, heat from the stove is transferred to your hand through conduction.
How does convection contribute to weather patterns?
Convection currents in the atmosphere transport heat and moisture, influencing weather patterns and the formation of clouds and precipitation.